All devices connected to the Internet have an IP address.
In simple terms, Internet protocol (IP) is the set of rules and formats that allows information exchange between these devices.
IP addresses are identifiers that allow one to locate other devices in the network and communicate with them.
Today, most of the internet traffic is being routed using the Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4), which was designed back in 1981 and implemented in 1982-1983. IPv4 has a limited supply of around 4.3 billion addresses, a large part of which is reserved for special network purposes.
IPv4 address space exhaustion was expected since the beginning of extensive Internet growth at the end of the 1980s.
As a measure to prevent this, version 6 of the protocol (IPv6) was designed in 1998, but even after almost 25 years, the adoption level of IPv6 is around 34-38% worldwide and about 46% in the US.
IPv6 adoption happens mostly because of mobile network operators' efforts.
From the regular user perspective, the picture is even worse – just 30% of the top 1000 websites on the Internet are IPv6 compatible.
The low (around 4-5% annually) IPv6 implementation rate means that the IPv4 protocol is going to be in use for at least a decade. There is even more pessimistic research stating that full adoption of IPv6 will take as long as 32 years.
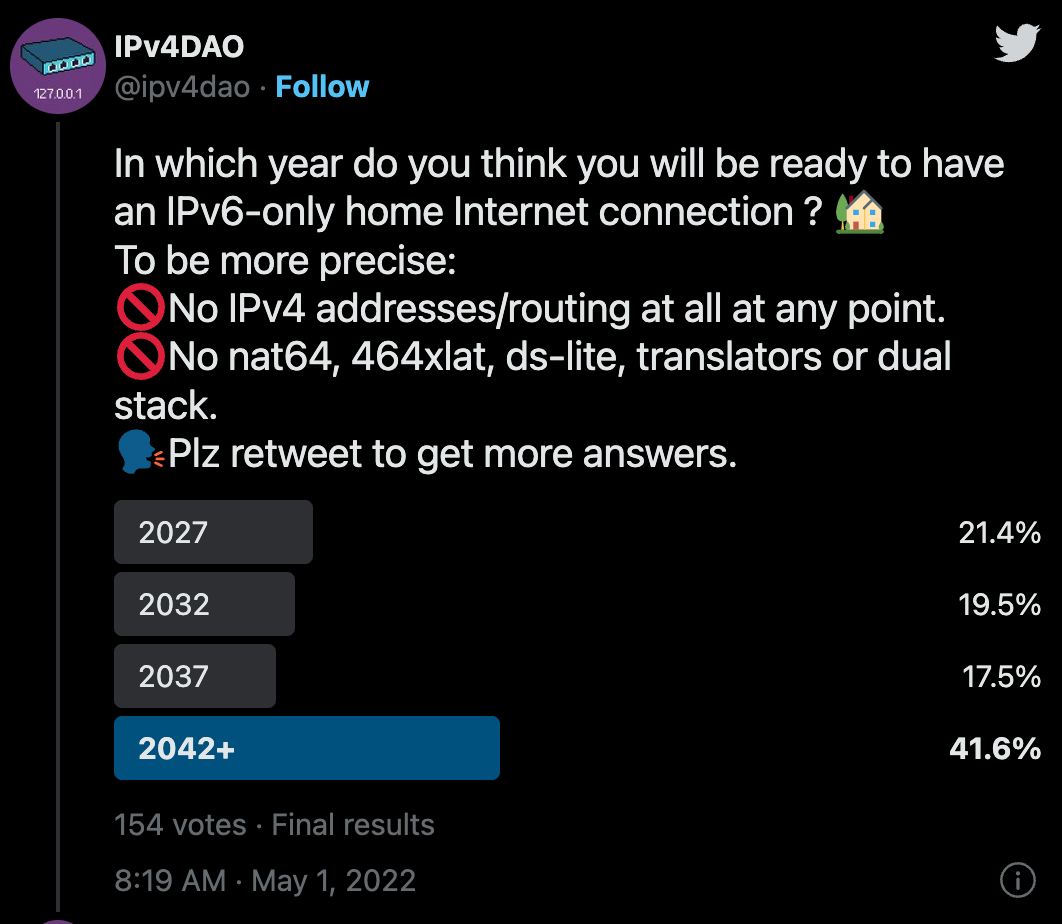
According to our recent survey on IPv4DAO Twitter, more than 40% of network enthusiasts voted that they think they would stop relying on IPv4 and switch to IPv6-only home connections somewhere after 2042.
IP address space is managed globally by IANA (International Assigned Numbers Authority) that distributes them regionally to five RIRs (Regional Internet Registries), which in turn distribute addresses to organizations such as local Internet Services Providers (ISPs).
On the global level, IPv4 addresses were exhausted in 2011, and on the regional level in 2019, meaning that there are no new IP addresses available, and you can only purchase them on the secondary market, from other organizations with excessive pools that sell or lease their unused IPv4s.
Current IP address distribution is largely the result of the ‘first come first serve’ approach that took place in the late 1980s-90s.
It does not reflect the importance of organizations or their need for IP addresses.
In the first half of the 90s, commercial organizations were able to claim to themselves entire /8 subnets, which are the largest subnet size available and contain more than 16 million IPs.
This results in sometimes anecdotal IP addresses distribution, when companies like Halliburnton or Xerox have 16 million IP addresses, and Elon Musk’s internet provider Starlink just 172 thousand.
Scarcity and uneven distribution of IPv4 addresses lead to various adverse effects, such as constant growth of costs, increased complexity of the processes around IP address allocation, and centralization of the ownership, which is the primary threat to the Internet as a structure and huge obstacle on the way of new technologies, such as web3 implementation.
The Internet in 2022 is far from being independent, decentralized, and publicly managed, and this situation will only worsen in the years to come. That is why we are creating IPv4DAO that allows us to introduce new approaches to IPv4 distribution and solve major problems caused by IPv4 scarcity and unfair distribution.
Our mission is the Internet Protocol with decentralized ownership and community-based governance.
We will start from a small independent oasis on the Internet, to which we bring the latest standards of decentralization, transparency, agility, and security.
We will grow it to give the web3 ecosystem vital living space in this monopolized and exhausted desert of centralized IPv4 address space.
IPv4 is going to be with us for at least the next 10 years, with no signs of IPv4-related problems being solved.
In these circumstances we need to make every effort to ensure agility, cost-effectiveness, and openness of Internet development, securing it as the foundational layer for freedom and innovation.
That’s why it is crucial to create and implement technologies, processes, and organizational structures, that can guarantee the fair decentralized management of IPv4.
Successful realization of IPv4DAO goals will ensure the following benefits for the Internet.
The ownership of IPv4 will be spread among Internet users.
The power of blockchain technologies will guarantee equal access and traceability of decision-making, as well as provide information on resource usage and allow redistribution of network assets to critical projects.
In the future, this approach will help us to solve current legacy distribution, which was done mostly decades ago and in favor of old US tech companies.
A lot of these companies have been stacking IPv4 addresses for years, not using them, and not gaining any value from the possession.
Our decision-making and discussions will be as open as possible.
To facilitate the knowledge transfer, our communication will remain accessible to future members of the community.
Resolutions will be immortalized in the blockchain.
Every major decision taken by vote will be imprinted in the blockchain to make it immutable.
This will set a new level of governance transparency and openness in one of the most important areas of our world.
Companies that possess a large amount of IPv4 addresses do not feel pressure or any urgency to upgrade to IPv6.
This results in fewer investments in a new routing tech which costs money, and they choose to optimize for profit.
This drags down the development of the entire Internet and creates an extra barrier to entry for the newcomers in the space.
Transfer of IPv4 management to the independent community will direct the benefits that can be obtained from IPv4 ownership to the development of Internet technologies, which in its way will result in benefits for all Internet users, and not just a handful of major companies.
IPv4DAO is an exciting experiment of community ownership of the vital Internet resource.
It will serve as a good example of managing critical intangible resources that should belong to everyone.
It will also set good practices for further decentralized, community-based management of public resources.
Moreover, this approach could also be applied to IPv6 in the future.
We will use the newest web3 tech to level up one of the oldest technologies of the Internet.
Multi-signature, decentralized governance, blockchain, generative art, NFT ecosystem – we will get our hands dirty with all of that.
Building a showcase of how web3 technologies help solve one of the longest-lasting Internet problems will serve a great purpose for building trust and adaptation of these technologies for dealing with real-world tasks.
By bringing decentralized IPv4 to the web3 ecosystem we will create new exciting possibilities for innovative projects from both worlds.
Even though the DAO community will choose the path of our journey, there are a few exciting challenges and opportunities that we can identify today.
First, we create a DAO to gather a community to rely on and define clear governance mechanisms.
This organizational structure would guarantee decentralized decision-making and protect this project from being overturned to one's sole interest.
After having DAO in place, its legal entity will allow us to register as a Local Internet Registry and acquire first decentralized IPv4 subnets.
While we are filling our pool with IP addresses, we decide on initial IPv4 pool monetization strategies as we will have some of them available from the start.
This revenue could be used to grow our pool and ensure further protocol development.
Once we have initial IPv4 addresses in our pool, we begin to develop the protocol.
We want to achieve fully automatic pool administration based on the blockchain.
One of the ideas is to bind each IPv4 subnet to NFT, which will serve as the main element in our protocol.
When the protocol is ready, we will explore different subnet-bound NFT rental techniques and ownership transfer scenarios.
Our next objective would be to create a web3 platform that will serve as an interface, facilitating the interaction with the protocol and providing access to our IPv4 address pool.
Due to the decentralized nature of IPv4DAO, the users won't be restricted to our platform as they will be able to control their IPv4 resources by interacting directly with the blockchain and without intermediaries.
Our web3 platform will only facilitate such interactions.
Our first challenge would be to organize ourselves in a DAO.
We are gathering a community interested in taking part in this ambitious project.
Each member will strive to provide an open, transparent, and comfortable environment for this community to thrive and expand.
The governance will be ensured through public discussions, proposal formalizations, and votes.
To guarantee transparent and secure voting, we will mint and distribute governance tokens that provide members with voting rights.
We may limit each member’s maximum amount of voting rights to ensure the even distribution of tokens and avoid a 51% attack.
Once we distribute initial DAO tokens we will set up an IPv4 address pool.
We are creating a non-profit company in Marshall Islands and register ourselves as a Local Internet Registry(LIR) in some of the Regional Internet Registries.
Being a LIR would allow us to acquire the first dormant IPv4 addresses through the brokers.
Having a legal entity would help us to start leasing out our first IPv4 subnets almost immediately after that.
We would use the revenue from this lease to acquire new IPv4s, cover the expenses and ensure the protocol development.
Our protocol will wrap each IPv4 subnet with a token.
The result would be a subnet-bound NFT.
One token will be attached to one IPv4 subnet.
The owner of the token will have control over the corresponding subnet.
The protocol will ensure the routing and management of every subnet based on such token’s state.
The owner would only need to adjust a few parameters of the NFT to route the subnet to the desired location.
We would start from basic routing operations such as bringing your IPs to AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, and other clouds.
As we provide a decentralized solution there won't even be a need to interact with IPv4DAO to exercise the control of the subnet.
The owner of such subnet could simply write desired changes to the blockchain in the most suitable way.
We would also create a web3 platform that will serve as an interface for our protocol.
It will allow subnet-bound NFT owners to perform routing operations from their browsers through a user-friendly interface.
Imagine a web app that connects to your web3 wallet to fetch your subnet-bound NFTs. Through its interface, you could perform the desired action on your subnets.
Maybe you’ll want to lease them or route them to a different data center.
Once the changes are done you confirm the transaction through your wallet and the state of the NFT changes.
After that our protocol automatically does the rest.
Simple, right?
